

Index Home Desert-Electricity World Deserts Electric Network Types of Produktion Comparison Water Network Hydrogen New Industry Green Cities Energy Transition Imprint
Waternetwork
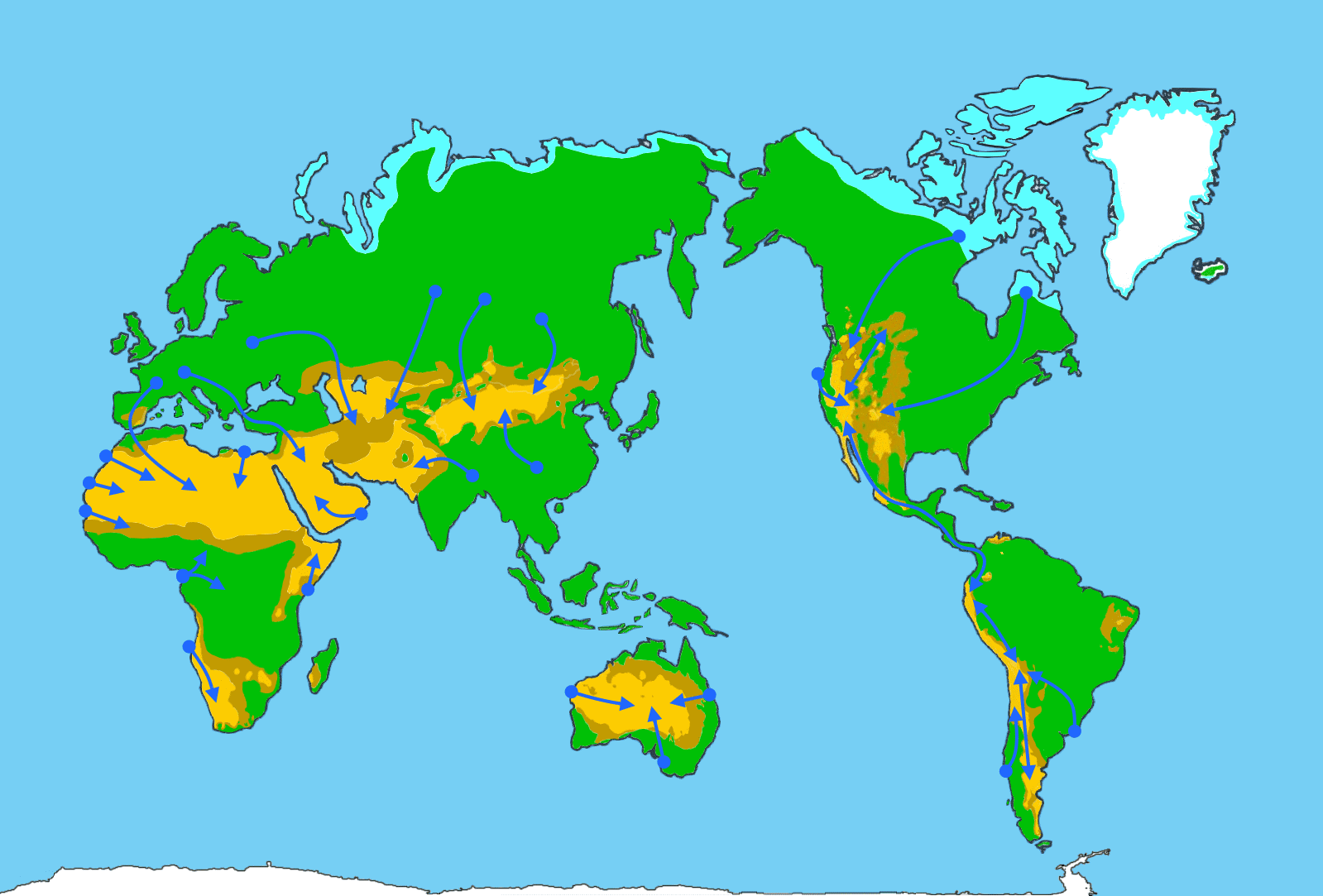
The international water network is now about creating balance on different levels and transporting water to the dry prayers of the earth.
1. UNESCO writes in its study that almost half of the world's population lives in areas where there is too little water for at least one month per year. Water shortages currently affect around 3.6 billion people.
2. In the USA, important growing areas are increasingly lying fallow because there is a lack of water. In Morocco, the most beautiful oases in the world are becoming salty because the groundwater level continues to fall. In Chile, entire villages are supplied with drinking water by truck because the avocado farmers use so much water that the surrounding small farmers and village communities no longer have any water. Entire rivers dry up there.
3. Heavy rain is increasingly affecting many regions, and floods can now be recorded in winter and in the interior of the country. Nevertheless, the groundwater levels are falling in the same regions, the reason being that the water flows via the rivers directly into the oceans because the earth cannot absorb all that much water at once.
4. The world's deserts are becoming ever more widespread due to global warming. In order to stop this process, green zones would have to be set up, which would require water there on site.
5. For hydrogen production on site, directly where it is used, but also for agricultural use, large water pipes are also needed in the interior of the country, because you cannot continue to exploit the groundwater reserves without endangering drinking water production and green growth.
Seawater desalination and diversion
One way to address this problem is to desalinate seawater and direct this water inland where, if fields and other areas are artificially irrigated, the groundwater would be replenished or no longer exploited. This solution is already being used all over the world. The resulting amounts of salt are still being returned to the sea, which increases the salt content in the sea and threatens fish stocks, corals and aquatic plants.
The salt is no longer allowed to get back into the sea and so research is currently being carried out at high speed into using salt with binding agents as a building material. The successes so far can be seen and the positive properties of salt can be used very well in the construction sector.
Reverse osmosis versus boiling salt works
We should no longer use reverse osmosis but boiling salt works. The salty water is heated with solar energy on flat stainless steel tracks that are enclosed in glass. The water evaporates and the pure water vapor is collected in tanks. This technology reduces CO2 emissions by 1400 percent compared to reverse osmosis.
This method uses hardly any external energy and, above all, no chemicals. This process produces little non-toxic brine or no waste water at all because salt is extracted at the same time. In addition, various minerals such as calcium, magnesium, sodium, chloride and even lithium can be extracted from this brine through so-called nanofiltration.
In order to produce drinking water, however, we have to add important minerals to the water, so some of the minerals extracted are used again. If the water is used to irrigate fields or to fill groundwater reservoirs, mineralization may not be necessary, as natural fertilizer is usually added or the water absorbs minerals from the soil. By the way, the sea salt extracted is of high quality and very popular. Rock salt from mines is definitely of lower quality. Chefs all over the world swear by sea salt. There are even special desalination plants that produce sea salt foam, the so-called Espuma de Sal. The same applies to Flor de Sal, the flower of salt, a layer that forms on top of the brine in the last basin and is skimmed off by hand. The global salt consumption alone would justify this method, as it could be covered with high-quality sea salt.
Another way of distributing water is to divert water from potential and future flood areas, from rivers before the water reaches the sea, to storage areas and from there to dry areas for irrigation new cultures.
This requires a water network that is able to distribute water intelligently and of course it also requires a lot of low-emission energy that must be accessible anywhere in the world. Research must be directly involved here in order to avoid future mistakes because even if we want to correct deficiencies and problems, we in turn intervene in the natural cycle and this intervention must be constantly monitored and corrected if necessary.
For example: If we artificially irrigate fields and other plantings, they must of course not be further contaminated with artificial fertilizers, pesticides, fungicides, herbicides and insecticides, as these poisons would end up in the groundwater and thus poison the later drinking water. This must be avoided at all costs.
This is the only way we could permanently solve the earth's problems, which were not only created by us humans in the 19th century.
Index Home Desert-Electricity World Deserts Electric Network Types of Produktion Comparison Water Network Hydrogen New Industry Green Cities Energy Transition Imprint