Index Home Desert-Electricity World Deserts Electric Network Types of Produktion Comparison Water Network Hydrogen New Industry Green Cities Energy Transition Imprint
Comparison with other electricity generation methods
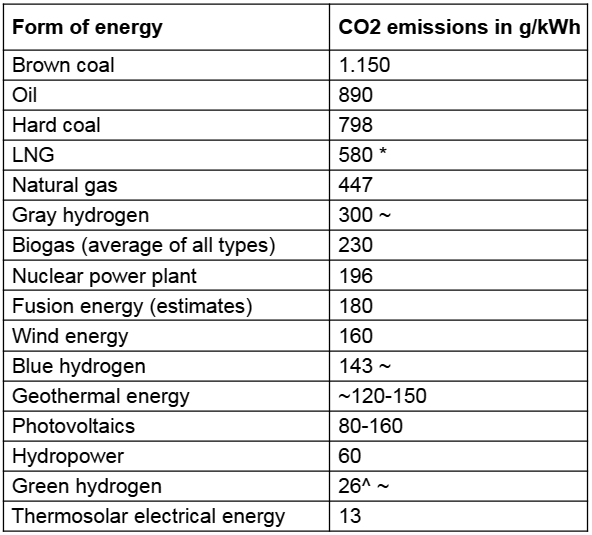
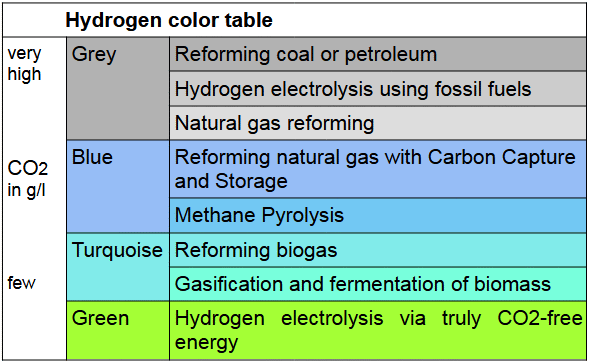
There are countless different statistics about the different types of production. In almost all types of electricity generation, a wide variety of factors are ignored, such as the fact that reservoirs also produce CO2 or that CO2 and toxins are also produced when disposing of wind turbines and photovoltaic systems. When it comes to photovoltaics, for example, values from southern countries are often used to make the CO2 balance more beautiful. With biomass, plants generally grow with fertilizer, the production of which produces CO2; this does not appear in any balance sheet. The livetimes of facilities are also not included in the balance sheets. After around 25 years, wind turbines become expensive hazardous waste and need to be replaced. This whole obfuscation is clearly just about selling something, like facilities, opinions and feelings. So it is very difficult to determine what is really green and sustainable.
But by far the best form of generating electrical energy is thermosolar generation via parabolic mirrors in the world's deserts. The decisive factors here are the technical simplicity, the low price for setting up a solar power plant, and the fact that a solar power plant does not require any fuel. the really extremely long running times and the high recyclability of such systems. Connected in an international network, these power generators can supply enough energy for all applications at any time of the year and at any time of the day, and so on-site hydrogen electrolysis suddenly becomes sufficiently low in CO2 and also the electricity generation via hydrogen power plants is suddenly a good alternative if the network does not provide enough power. Above all, this is the only way a truly green, energy-intensive industry is possible. Everything else is crazy fantasies that lead us nowhere.
All types of production at a glance


The World Energy Report 2023
After the consumption of fossil fuels decreased during the Covid 19 pandemic, it is increasing exponentially again in 2021.
The world energy system remains virtually unchanged; Current trends are still clearly not sustainable. An energy revolution is necessary in order to ensure a reliable and affordable energy supply, and on the other hand, existing production must be converted so that it becomes sustainable and environmentally friendly.
This is what the OECD's International Energy Agency (IEA) says in its latest world energy outlook. But how this is supposed to happen is not even hinted at.
What is certain is that poorer countries take little or no part in change. Since these are mainly southern countries, they could benefit from an energy revolution via solar energy, for the benefit of the entire Earth community.
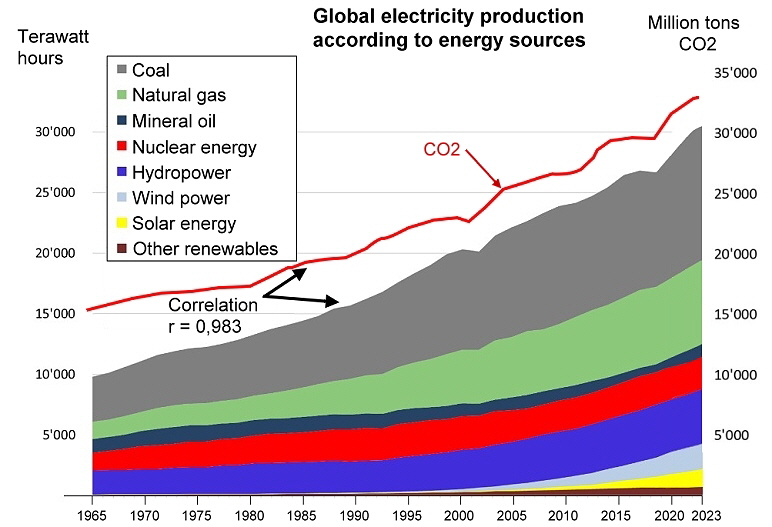
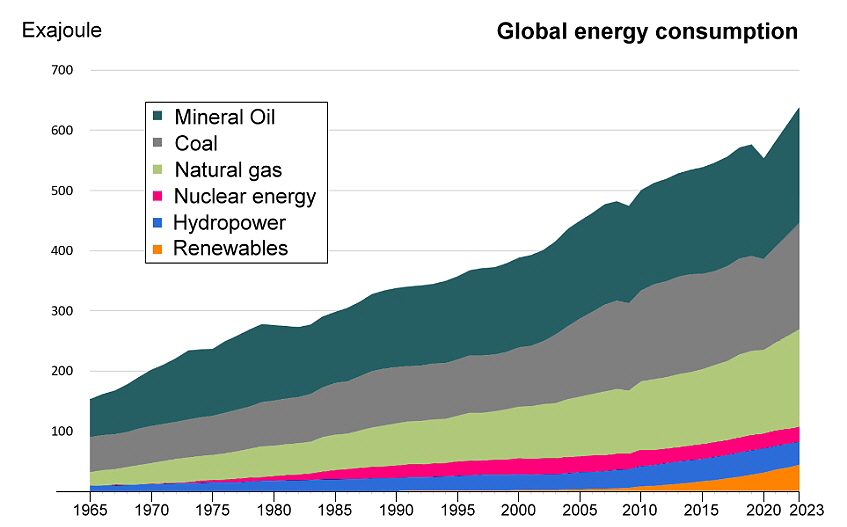
Whatever they like to tell-sell you, it has happened as good as nothing. All previous efforts regarding renewable energies have been more than negated by the increased production worldwide. The consumption of fossil fuels and the CO2 content in the atmosphere continue to rise exponentially. The heat storage capacity of the oceans has been exhausted, and from now on the heat is stored directly in the atmosphere. If there is now no real movement instead of “talk and advertising”, the consequences can no longer be remedied. It's no longer about "make our country great again" but about survival.
Biogas:
Biogas is an energy source that is produced regionally from various raw materials. In addition to manure and green waste, this also includes energy crops that take up space in the food chain. The gas is produced in so-called fermenters, in which the raw materials ferment. Depending on the material used, the bacteria produce biogas with a methane content of 50 to 75%. This is very problematic because methane is much more dangerous than CO2. An average of 230 g/kWh CO2 is released when using biogas, which is about a quarter of natural gas, but still a CO2 and also a methane producer. The remains of the fermentation, which is usually a brown, foul-smelling paste, must then be disposed of. Because of its high nutrient content, it is mostly used as an agricultural fertilizer, which then contributes to soil salinization, but is at least better than artificially produced mineral fertilizer. Soil salinization is one of the greatest ecological risks of the 21st century because it makes soils increasingly infertile. Climate change and agricultural practices such as artificial irrigation and over-fertilization are driving this process. Researchers at the TU Hamburg warn of fatal soil degradation by the year 2100 if no countermeasures are taken.

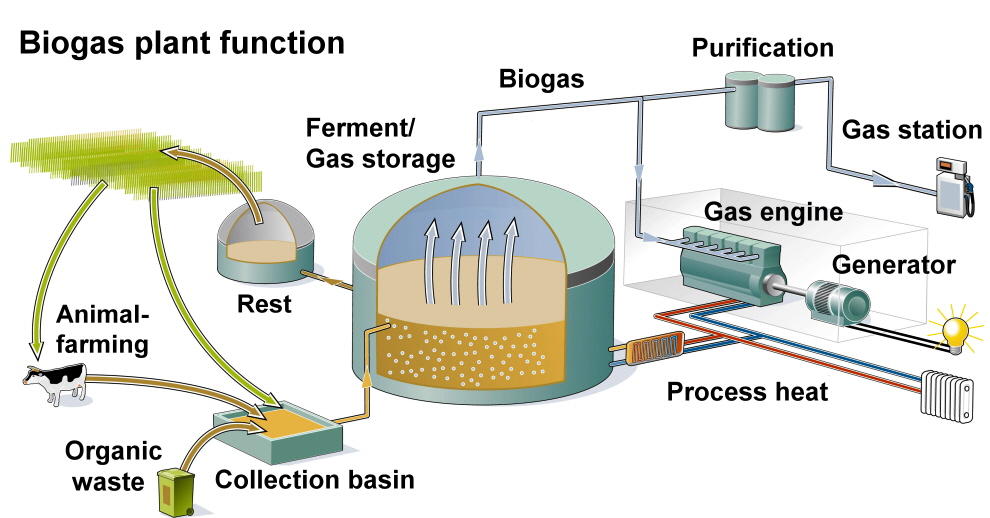
Conclusion:
Biogas is not an ecological form of energy, it is rather a method of getting some money out of the end products of factory farming, the gases from garbage dumps and sewage treatment plants. It would be better to look for solutions to the problems created by modern agriculture, factory farming and the insane waste management of the 21st century instead of making the problems create more problems. To claim that biogas is, so to speak, climate-neutral, because CO2 would be bound beforehand through the permanent overproduction of everything, is a big mistake because all of these products grow with the help of nitrogen-containing fertilizers, which in turn produce CO2. However, it is an outrage and against nature to grow plants specifically to produce biogas or biofuel.
Geothermal energy
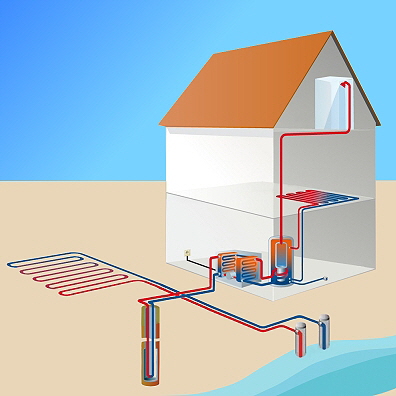
The term geothermal energy refers to both the thermal energy stored in the earth and its technical use. Since it is generally available continuously and is subject to only minor fluctuations, it can be used reliably for heating and generating electricity, but also for cooling. In contrast to other renewable energies, geothermal energy is available almost at any time, regardless of the climate and the time of year and day. The Earth consists of different layers with different temperatures: The core is the hottest part at 4,800 °C to 7,700 °C. By depths-geothermal energy we therefore understand the generation of energy from the very high temperatures that exist below the earth's surface in the deeper layers of earth and rock as well as in underground water reservoirs.
In order to obtain thermal energy from so-called near-surface geothermal energy closed pipe systems are laid in boreholes. Water is continuously pumped around. The water absorbs the underground heat and is brought to the required temperature on the surface using heat pumps. This increases the efficiency of the so-called heat pumps by a few percent. Systems that tap underground water reservoirs are dangerous, they change the water temperature which can lead to unexpected reactions.
Depths-geothermal energy is not suitable for regions where earthquakes are more common. To use thermal energy, it is necessary to drill holes in the ground. These are usually deep holes that are several kilometers long.
The largest geothermal power plant in Russia is located 60 km south of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky on the banks of the Falsivaya River. The capacity of the power plant is just 50 MW. It is operated by Geotherm JSC, a subsidiary of PJSC RusHydro.
Which countries produce the most geothermal energy?
The USA continues to produce the most geothermal electricity, closely followed by Indonesia, where production has increased significantly. Kenya and Turkey also recorded strong growth.



Does geothermal energy have a future?
Geothermal energy is not a bad thing, but it is too expensive and its construction involves a lot of CO2. In addition to near-surface use, around an eighth of the heat requirement could be met from much deeper layers of the earth. However, deep geothermal energy is technically demanding and not without risks.
That's why we shouldn't overdo it with geothermal energy production because of the disadvantages.
What are the disadvantages of geothermal energy?
1. Restricted location.
2. Significant ecological side effects.
3. Earthquake.
4. High costs.
The mistakes
We have made mistakes, mistakes that cannot be easily reversed. In order not to fall into the same traps again for certain reasons the quick profit, we have to talk about them and highlight the realities. The four greatest natural hazards of the post-fossil era were specifically selected: The nuclear energy, the fusion energy, the wind power and the photovoltaics.
All of these types of electrical energy generation are usually extremely expensive, require a disproportionate amount of unreliable technology, require a lot of space in populated areas and are sometimes there very dangerous. The production of this complex technical device continues to release an extremely large amount of CO2 and ultimately, after a relatively short period of use, there remains extreme amounts of hazardous waste. Garbage which destruction or partial reuse also generates an extreme amount of CO2 and toxins. With all of these techniques, there is ultimately a lot of residual waste or residual toxic substances left over that has to be permanently stored in hazardous waste landfills, sometimes for thousands of years. In addition, some of these types of production significantly contaminate or endanger nature during operation or at least disrupt the natural process.
You are therefore welcome to find out more about the concerns here.
Index Home Desert-Electricity World Deserts Electric Network Types of Produktion Comparison Water Network Hydrogen New Industry Green Cities Energy Transition Imprint